Abstract
Background: The multiple myeloma (MM) treatment landscape is continuously evolving. Many treatment regimens are available as combination regimens. Currently, real-world evidence on treatment patterns and outcomes in relapsed/refractory MM are limited, particularly in second (2L) and third (3L) lines of therapy (LOT). This study aimed to describe standard of care for 2L and 3L MM treatments by calendar year (prevalent cohort) from 2018‒2020 and among patients initiating 2L or 3L treatments (incident cohorts) between 2018‒2021.
Methods: This retrospective study utilized de-identified patient-level data from Flatiron Health, a nationwide, longitudinal, demographically and geographically diverse database derived from electronic health records originating from over 280 cancer clinics, primarily community-based. The prevalent cohorts were assessed in each study calendar year, and patients had received ≥1 non-maintenance, non-transplant MM drug in 2L or 3L during 2018, 2019, or 2020. Patients in the 2L and 3L incident cohorts had a MM treatment start date for their respective LOT between January 1, 2018, and April 30, 2021. The index date was initiation date of 2L or 3L therapy, respectively. Patients in each LOT were followed for at least 90 days from the index date. Patients with non-MM cancer treatments or investigational cancer drugs were excluded.
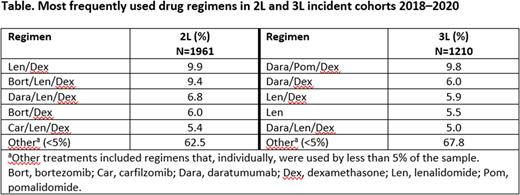
Results: Over 2018‒2020 in the prevalent cohorts, the most frequently used regimen in 2L was bortezomib/lenalidomide/dexamethasone (VRd) at 13‒10%, and in 3L was daratumumab/pomalidomide/dexamethasone (DPd) at 8‒11%. In the incident cohorts, patient characteristics were similar between the 2L (mean age 69 years, 54% male) and 3L (mean age 69 years, 53% male) groups, except for higher prior use of daratumumab in 3L (16%) compared with 2L (1%). The most frequently used treatment regimens are shown in the Table. In 2L incident patients, lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd) was the most common treatment at 10%, while DPd was the most common 3L regimen at 10%. In both LOTs, immunomodulatory drugs (2L: 64%; 3L: 61%) and proteasome inhibitors (2L: 58%; 3L: 48%) were commonly used. Triplet therapy was commonly used in both 2L (47%) and 3L (47%).
Conclusions: This study provides insights into real-world treatment patterns among patients initiating 2L or 3L in community-based cancer clinics. While triplet regimens were a frequent approach in both 2L and 3L treatments, there is a wide variation in the regimens used.
Funding: GSK (214295)
Disclosures
Boytsov:GSK: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Gorsh:GSK: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Anderson:GSK: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Wang:GSK: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Perera:GSK: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Franklin:GSK: Consultancy, Other: President of Franklin Pharmaceutical Consulting, which received funding from GSK to develop the study report.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal